What is a Knowledge Graph? | Yext Hitchhikers Platform
What You’ll Learn
In this section, you will learn:
- What a knowledge graph is
- How a knowledge graph powers consumer experiences on search, business listings, and webpages
What is a Knowledge Graph?
A knowledge graph is a database that is designed to structure data objects and the relationship between those objects.
For example, a restaurant franchise (like Galaxy Grill — the fictional brand you’ll see across Hitchhikers) could use a knowledge graph to store data on objects like:
- Restaurant locations
- Menu items
- Services like delivery and takeout
- Job postings
From there, a knowledge graph could help the brand to create relationships between those objects:
- Menu items that are available at certain restaurant locations
- Which locations offer delivery
- Job postings by restaurant location
Why Use a Knowledge Graph?
The purpose of a knowledge graph is to power downstream experiences. A downstream experience is any application that can use structured data in order to build a user-facing experience.
These can include:
- Business listings on Google, Apple, and other major publishers
- Web pages
- Site search experiences
How downstream experiences use structured data
Structured data can be used to answer complex questions from consumers. As an example, let’s look at how structured data stored in a knowledge graph could be used to power a dynamic search experience.
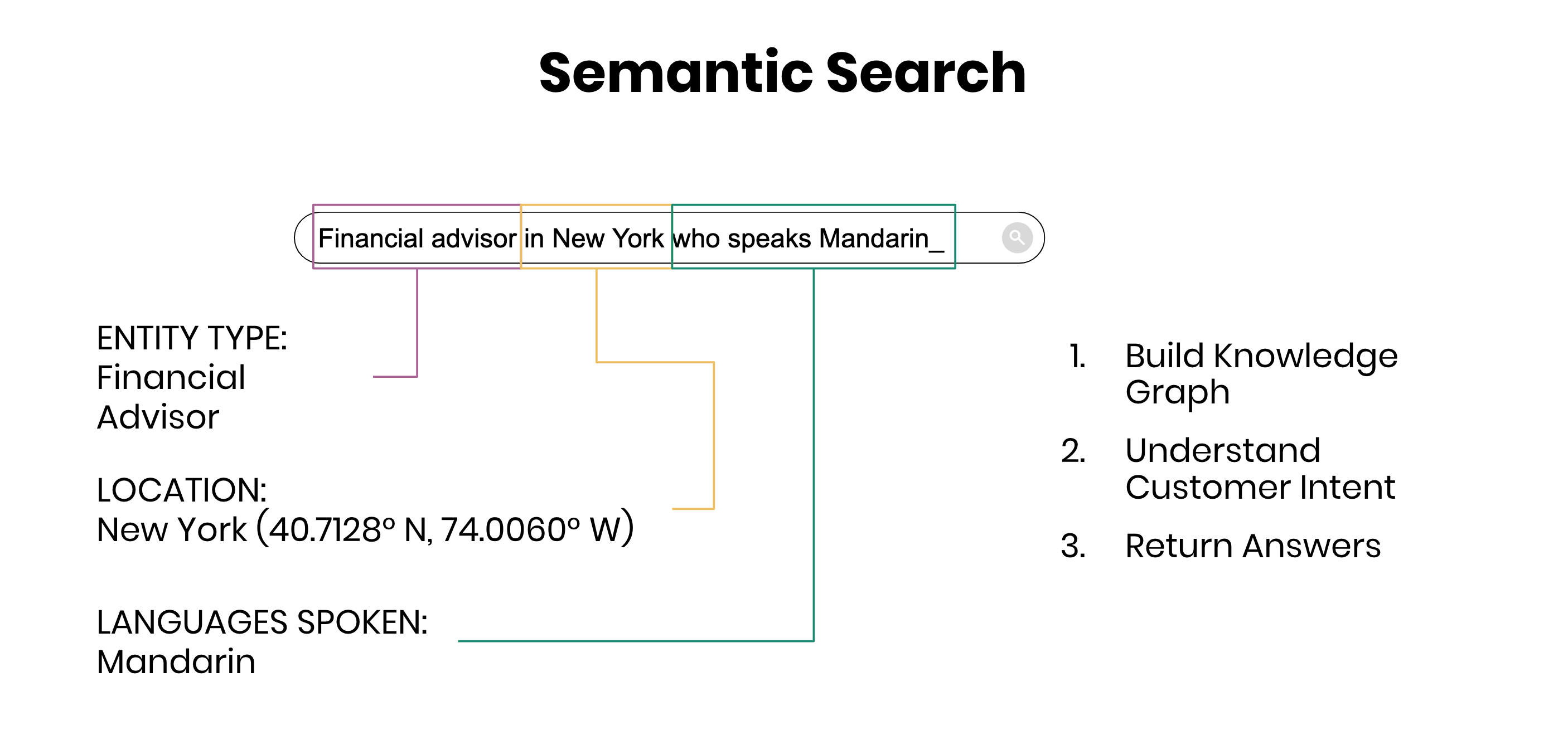
Take this example search: “Financial advisor in New York who speaks Mandarin”
This search query contains a few different data objects that are related to each other:
- a professional (financial advisor)
- a location (New York)
- a language (Mandarin)
If this data is not stored in a way that reflects these object relationships, a search engine may not be able to deliver accurate results.
Traditional index-based search may not be able to effectively handle queries like this, because it doesn’t account for the relationships between the different data objects.
For example, here is how a traditional keyword index search might parse this query:
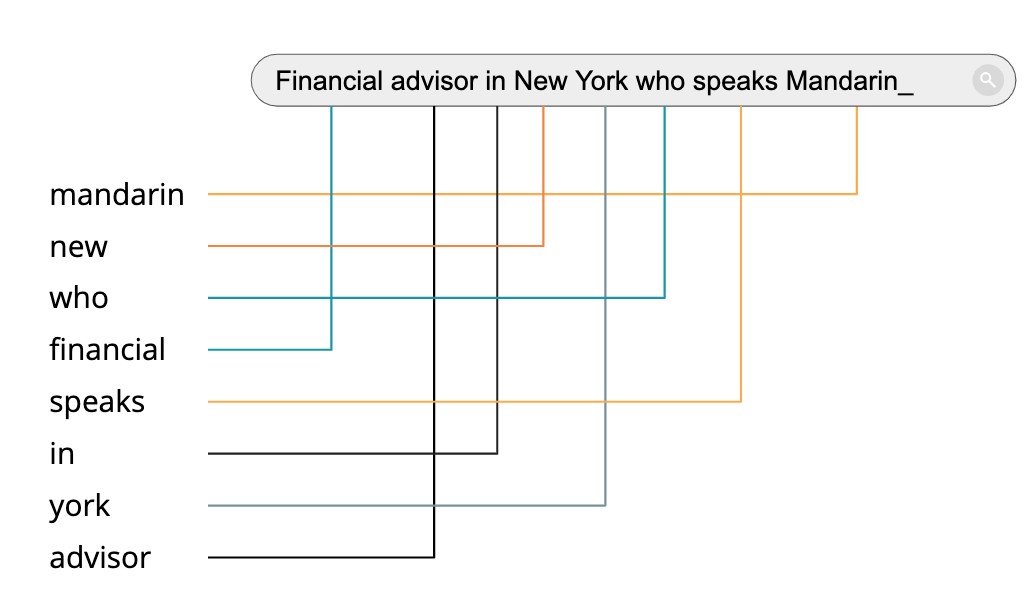

However, if this data was structured in a knowledge graph, that data could be used to build a semantic search experience. The results may look something like this:
In the next unit, you’ll learn about how objects and relationships are structured in the Yext Knowledge Graph, and how that structured data powers products across the Yext platform.
What is a knowledge graph?
Why are object relationships important when structuring business data?
High five! ✋

