Introduction to the Yext Knowledge Graph | Yext Hitchhikers Platform
What You’ll Learn
In this section, you will learn:
- What entities, entity types, and entity fields are in Yext
- How the Yext Knowledge Graph powers other Yext products, like Pages, Search, and Listings
What is an Entity?
In Yext, the data objects stored in the Knowledge Graph are called entities. Entities hold the data that is used to build downstream experiences in Yext Search, Pages, and Listings.
Each entity represents a real-world object that is a part of your business. Common examples of entities are:
- Locations (retail stores, offices, etc.)
- Restaurants
- Products
- Job postings
- Professionals (doctors, nurses, consultants, etc.)
- FAQs
Entities are also the core of the Yext platform: entity data is what you’ll use to power your business listings, build your website pages, and create search expereinces with Yext.
Entity Types
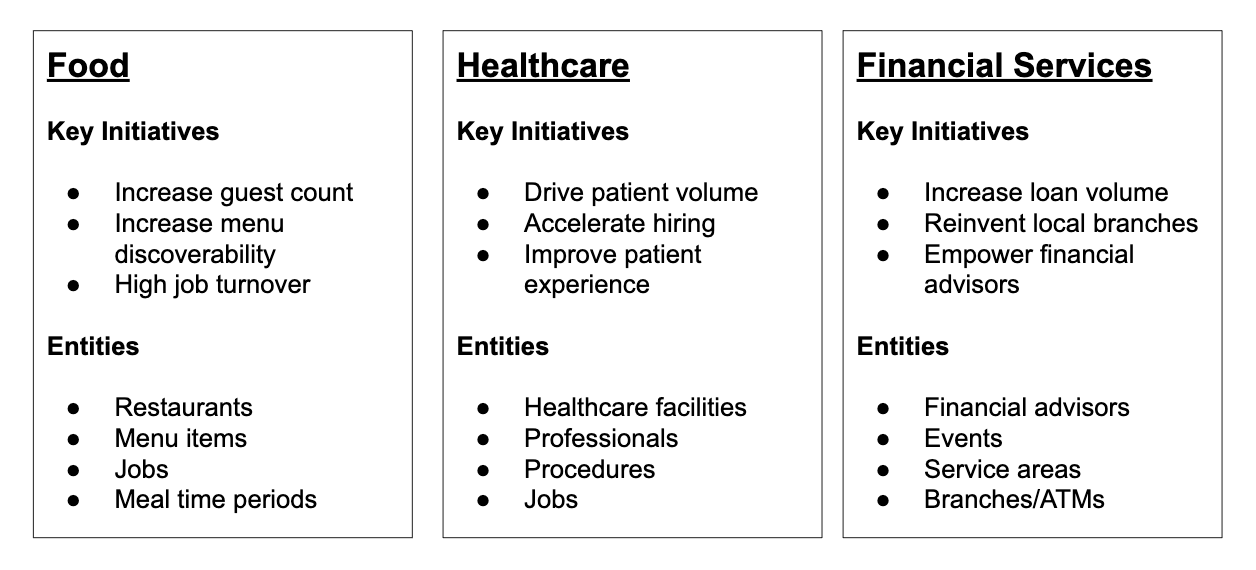
As shown in the examples above, each business will have different kinds of entities that can be stored in the Knowledge Graph. In Yext, you can define the entity types you want to use in your Knowledge Graph. You can then link different entities together to form the object relationships that will support your search experience, website pages, and listings.
Here are some examples of the entity types a restaurant, healthcare organization, and financial organization might decide to use in their Knowledge Graph:
Entity Fields
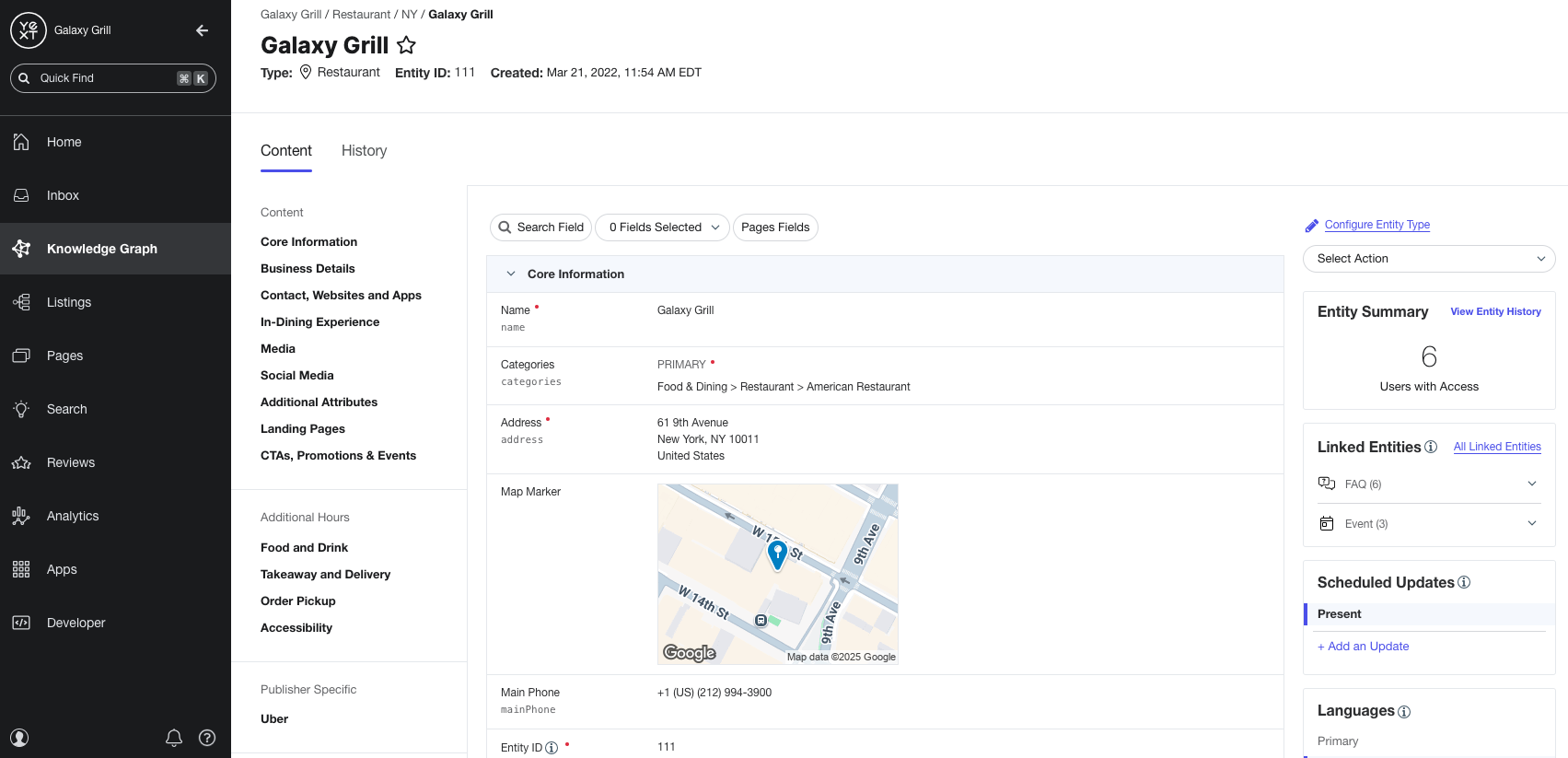
Each entity will also contain its own set of information. For example, a Restaurant entity might contain information like the business hours, address, phone number, and website. This information is stored in fields on each entity.
Here’s an example of what a Restaurant entity could look like in the Knowledge Graph:
Next Steps
In the next unit, learn how to navigate the tools in the Knowledge Graph that you’ll use to structure and store your entities.
What is an entity in Yext?
True or false: Entities are the core of the Yext platform.
Soon you'll be your brand's hero! 🎓

