Searchable and Display Fields | Yext Hitchhikers Platform
What You’ll Learn
By the end of this unit, you will be able to:
- Define searchable fields and list the two components that are needed to set them up
- Recall common use cases for when to use each search algorithm
- Configure searchable fields, including for entity relationships, and display fields
Overview
Now that you’ve defined your verticals at a high level, including the name and entity types it should include, we’ll dive into configuring what is returned. The first step is to specify which fields can be searched by each Search algorithm for each vertical. This is what’s called a searchable field. In this unit we’ll go into more detail on the algorithms you can index with, what searchable fields are, and how to configure them.
Intro to Searchable Fields
In the Search config, you’ll define which fields are indexed (or searched) by the Search algorithm in each vertical. These searchable fields then affect which results are returned to the user. For example, if you want users to be able to find restaurants that are near them, you’ll want to make the entity location searchable in the Restaurants vertical.
Make sure to designate at least one searchable field for each vertical – otherwise, the Search algorithm will have nothing to search on and no results will be returned!
When defining a searchable field, you need to specify two things: the field and the algorithm. The Search config UI has sections for each algorithm, so you’ll first choose which algorithm(s) you want to use, and then decide which fields should use that algorithm.
Choosing the Algorithm Applied
builtin.location), and document search are only available on the Advanced Search tier. Check out the
Search Tiers
reference doc to learn more about the features that are available in each tier.
The first thing you’ll need when configuring searchable fields is to decide what algorithms to use to search on each vertical. Think back to the multi-algorithm approach . Are you trying to search on structured data, semi-structured data, or unstructured data?
Each algorithm will search the content in the field it’s turned on for in a different way. The search algorithms you can use are:
- Keyword Search (
textSearch): searches for every token in the query; best for short text fields with varied content - Document Search (
documentSearch): uses keyword search on long-form content; best for long text fields whose values you want to be returned as featured snippets - Phrase Match (
phraseMatch): boosts an entity to the top of results when there is an exact match between the query and the field content - Semantic Search (
semanticTextSearch): searches for semantically similar content - Inferred Filter (
nlpFilter): filters for the best exact match, is thus very restrictive, and best for structured enum/option fields with finite variations
For example, the inferred filter search algorithm filters for the best exact match and is thus very restrictive. Keyword search, on the other hand, looks for keyword matches in the content and is more flexible. Semantic search adds some natural language processing to understand the user’s intent beyond just matching on keywords.
Learn more about each algorithm and further configurations in the Search Config - Verticals reference doc. When multiple fields have Keyword Search or Document Search algorithms enabled, you can add field-level weighting, which allows you to assign boosts to fields. There are special inferred filter use cases to allow you to search on location, entity type, and hours.
When choosing which search algorithm to use, you’ll need to decide which one best fits the contents of the field and the purpose of making that field searchable. For best practices on how to approach choosing search algorithms, check out the Searchable Fields Best Practices reference doc.
Legacy Searchable Field Types
While technically considered filters and sorting, not searchable fields, the following were previously defined as searchable field types. In the updated config UI, you’ll find them in the appropriate sections, but if you are editing via the JSON editor, you’ll need to enable these searchable field types in the searchableFields object.
- Facet (
facet): allows a field to be used as a dynamic filter that a user can interact with to narrow their search; best for structured enum/option fields where there are a finite number of variations across entities. Learn more in the Facets and Filters unit. - Static Filter (
staticFilter): viewable “pre-search” and are not dependent on the search query. Learn more in the Facets and Filters unit. - Sortable (
sortable): allows a field to be used as a sorting method that is controlled by the algorithm or by the user. (Fields added to sorting via the UI will be configured as sortable automatically. Fields added to sorting via the JSON editor must be marked as sortable). Learn more in the Sorting unit.
Defining Fields
Once you decide which algorithms you want to use to search a vertical, you’ll need to specify the fields you want to search. For each vertical, you can pick from the fields available in the Knowledge Graph for the relevant entity type(s) (or Add Custom Fields and populate them if the content doesn’t yet exist in the platform). Each entity type that you set up in the platform has both built-in (profile) and custom fields associated to it. Both can be marked as searchable.
In the JSON instance of the Search configuration, fields are referenced by their API name (check out the
View Field API Name
help article to learn how to find this). These API names are also listed under the field name when adding fields via the UI. Any custom fields will have a prefix of c_ and any built-in fields will not.
Entity Relationships
You can also use linked entities as searchable fields to search for content on entities related to the ones you want to return in your results.
In the case of a restaurant chain, a location may be limited to only showing menu items with multi-option select or text-type fields (and any data changes would need to be made manually within the field). However, relating or linking Menu Item entities to Restaurant entities allows customers to see other relevant information about dietary restrictions or ingredients of specific menu items to help them choose a location that best serves their needs.
When referencing data from linked entities in Search, use dot notation (.) like so:
[[customRelationshipFieldID]].[[fieldName]]
In the example above, you may add a relationship field on Restaurant entities that links to Menu Items. To return the name of menu items sold at a specific location, use something like this:
c_relatedMenuItems.name
You can even use fields from a linked entity of a linked entity, or a multi-hop relationship. For example, in a Doctors vertical, you could link conditions to a specialty that is also linked to a doctor. This would allow patients to search for conditions and get results for Doctors that treat them even though those entity types aren’t directly related.
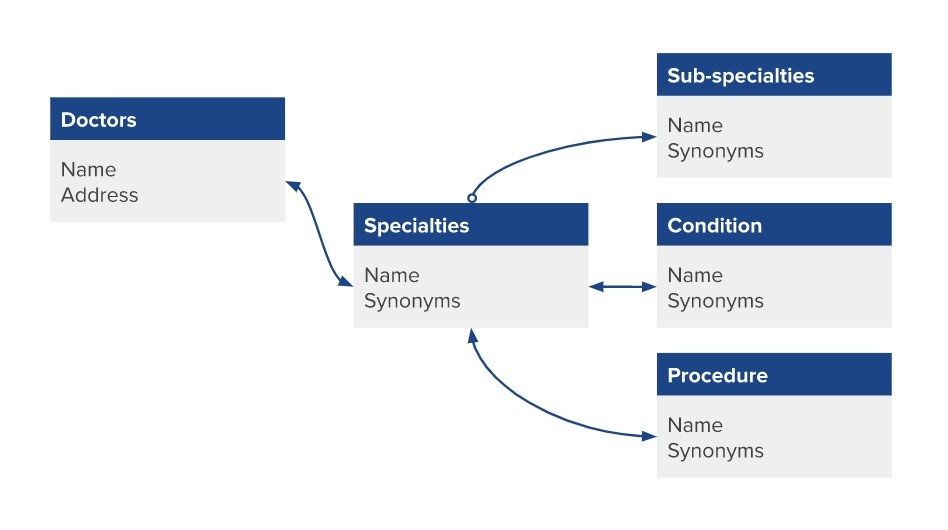
Note, in the Search config UI, you can only add the name field of related entities. To add other fields or multi-hop relationships, use the JSON editor. Use dot notation for every linked entity relationship.
{
"verticals": {
"ce_doctors": {
"searchableFields": {
"c_relatedSpecialties.c_relatedCondition.name": {
"nlpFilter": true
}
}
}
}
}Events Example
There are four searchable fields in the Events vertical we set up:
- Inferred Filter on the Entity Type (
builtin.entityType) - Inferred Filter on the Location (
builtin.location) - Phrase Match on the Keywords field (
keywords) - Semantic Search on the Name field (
name)
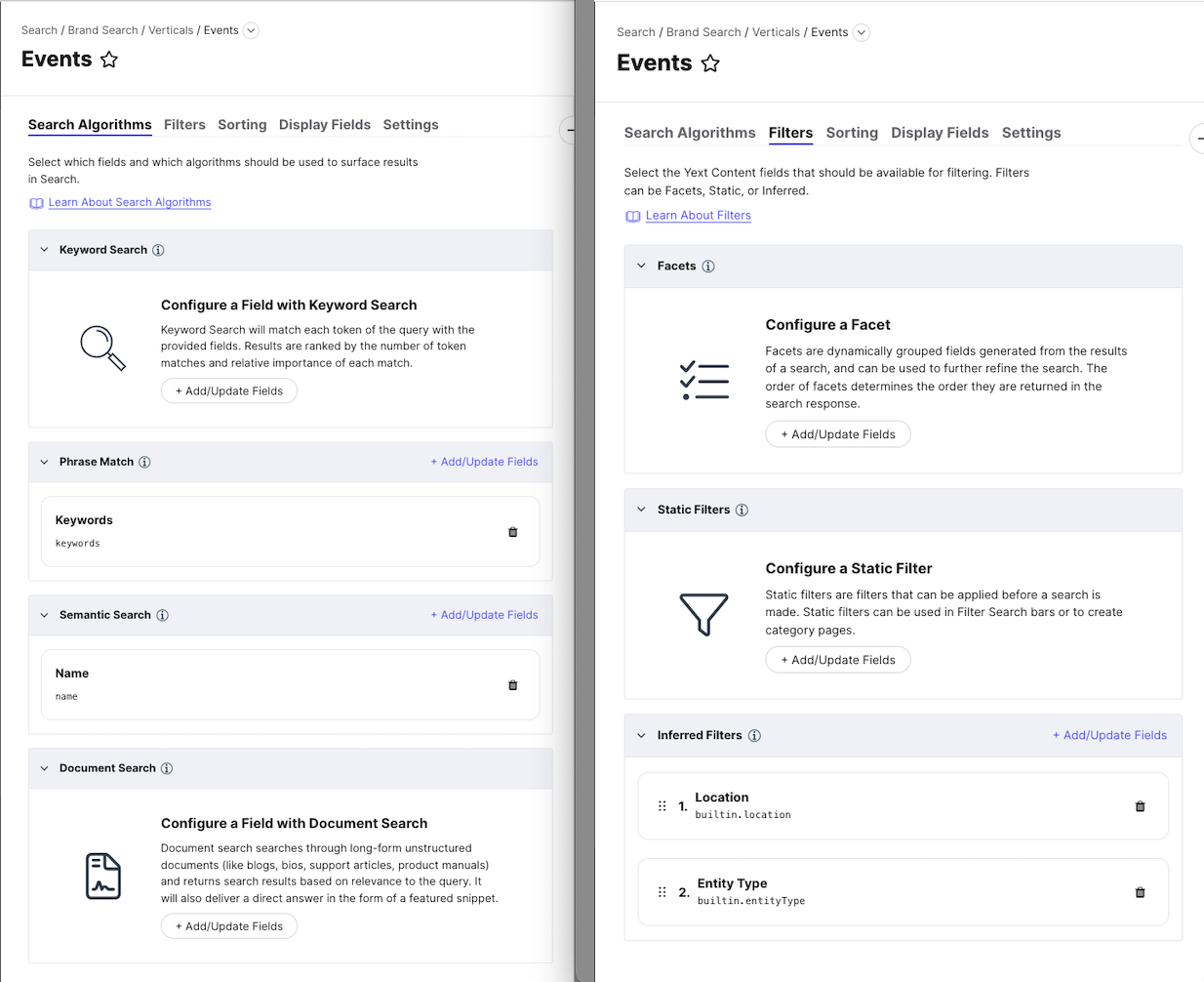
Let’s break this down:
Inferred Filters create a black and white filter with the best exact match. The inferred filter on entity type will return the Events entity type for search queries that contain “events.” This is a built-in value you can use with inferred filters only.
The inferred filter on location is another special case that enables location search on entity types with an address. This will return results for searches on “near me”, addresses, zip codes, cities, and other parts of the address based on proximity to the users’ location (rather than matching on the exact terms in the search query).
Phrase match allows an entity to be surfaced only when there is an exact match on the phrase in the query. This is good for keywords which are more free form and can include generic words that may match to content easily. This way, the keywords only get triggered if there is an exact match. For example, you may have an event with the keyword “taco Tuesday” and another with the keyword “taco Thursday.” You want to only surface the event if the whole keyword is queried, so you use phrase match. This will prevent both events from surfacing if the search is just “taco.”
Semantic search matches a query that is close in meaning, so it doesn’t have to be an exact match. In general, name fields (except on location entity types) are a good use case to use semantic search because users are likely to search for terms close in meaning without knowing the actual name. For example, you may have an event called “Steak Night.” You’ll likely want this event to surface for the query “beef burritos” as “steak” and “beef” are semantically similar.
Edit Searchable Fields
Edit via the Platform UI
To configure searchable fields in the UI, navigate to the Verticals screen, choose the desired vertical, and then select the Search Algorithms tab (selected by default when you go to the vertical). Find the search algorithm you want to use. Add a field by clicking + Add/Update Fields in the top right of the section to bring up a field modal and check off the fields you want to include. Uncheck any fields you want to remove, or click the trash can icon next to the field on the Search Algorithms screen.
Note that inferred filters are found on the Filters tab. We’ll talk more about filters in the Facets and Filters unit.
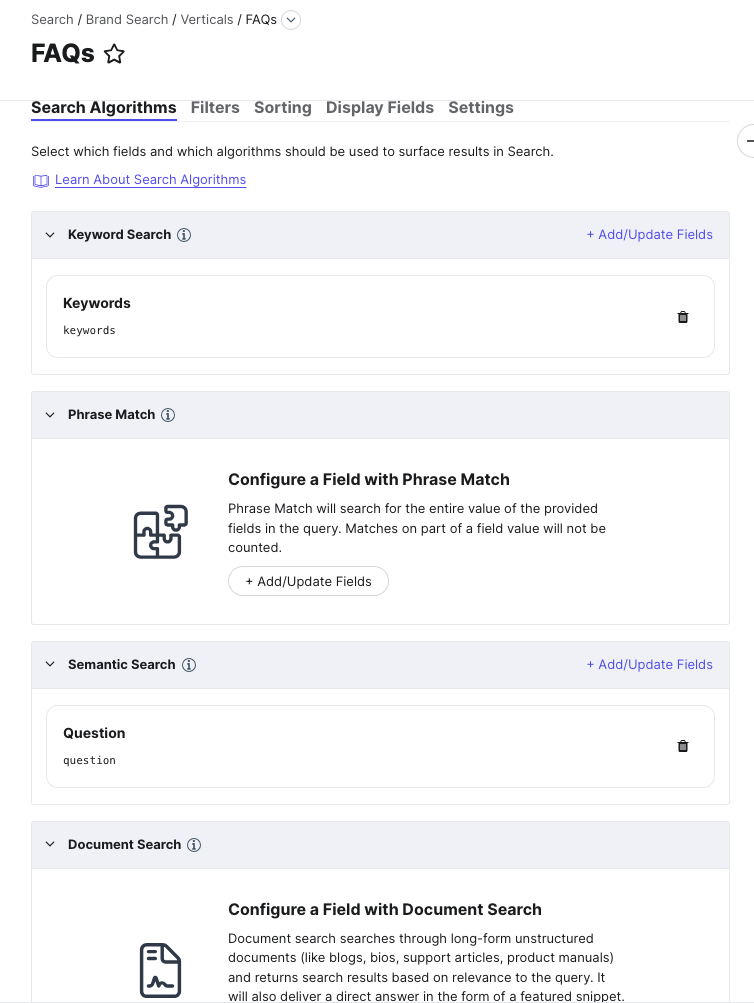
In the example FAQs vertical below, we’ve set up the following searchable fields:
- Keyword Search on Keywords
- Semantic Search on Question
Edit via the JSON Editor
In the JSON instance of the Search configuration, fields are referenced by their API name (check out the View Field API Name help article to learn how to find this). To set a field as searchable, specify the API Name of the field you are setting along with the search algorithm(s) you’d like to use. Find more details on each search algorithm in the Search Config - Verticals reference doc.
The JSON for the same FAQs vertical searchable fields configuration above would look like the following:
"verticals": {
"faqs": {
"searchableFields": {
"keywords": {
"textSearch": true
},
"question": {
"semanticTextSearch": true
}
},
"sortBys": [],
"source": "YEXT"
}
}Display Fields
While you’re thinking about which fields to pass from your Knowledge Graph to your Search backend, you’ll also want to think about which ones to pass to your Search frontend. You can only display fields on the frontend if they are passed to the frontend by the backend via the Search API response.
By default, the Search API response returns all fields on the result entity, but not any fields of related entities. If you want to display fields from related entities, you can add display fields to specify the entity profile fields that are returned as part of the Search API response. If you do include display fields, Search will only return the fields that you provide in this property, even if they are on the result entity, so you will need to add ALL fields you want to display on the front end of that vertical, including from related entities as well as the base entities.
It is highly recommended that you configure display fields because only returning the content you need in the API response will ensure the Search API is as fast as can be. While this property doesn’t affect your backend and how results are returned, you’ll need to use it to get content to the frontend.
You need to be precise when specifying display fields, particularly for linked entities. If there is a particular subfield you are looking to use, specify that subfield exactly instead of the parent field. For example, if you want to display a doctor’s specialties on their result card, add c_relatedSpecialties.name to display fields, not c_relatedSpecialties.
c_relatedSpecialties and c_relatedSpecialties.name in the list of display fields.
Note that Search API responses return all display fields that ever exist on any version of the experience. For example, if version 45 has the “description” field as a display field, but the most recent version 49 does not, the Search API response would still return “description”.
Edit Display Fields
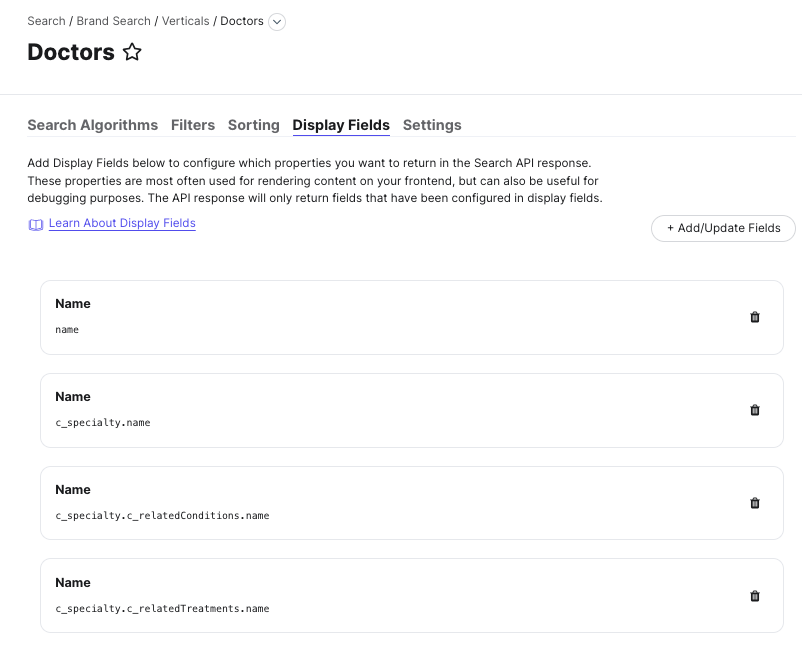
Let’s say, for example, that you are working on a doctors vertical, and each doctor is related to specialty entities that have lists of related conditions and treatments. You want to be able to display the names of those specialties, conditions, and treatments.
Remember that you should be precise and use the name subfields of the related entities, rather than displaying the parent field (the related entities themselves), so that the Search API response will return exactly what you need.
Edit via the Platform UI
To configure searchable fields in the UI, navigate to the Verticals screen, choose the desired vertical, and then select the Display Fields tab. Add a field by clicking + Add/Update Fields to bring up a field modal and check off the fields you want to include. Uncheck any fields you want to remove, or click the trash can icon next to the field on the Display Fields screen.
The above example would look like the following in the UI:
Edit via the JSON Editor
The JSON for the same doctors vertical display fields configuration above would look like the following:
"verticals": {
"doctors": {
"displayFields": [
"name",
"c_specialty.name",
"c_specialty.c_relatedConditions.name",
"c_specialty.c_relatedTreatments.name"
]
}
}Check out the Search Config - Verticals reference doc to learn more.
What are searchable fields?
What types of fields can you set as searchable? (select all that apply)
What searchable fields would you have to set up to return results that fulfill the entire query 'restaurants near me'?
What scenarios prompts you to add display fields (Select all that apply)?
Soon you'll be your brand's hero! 🎓

