Reverse Proxy | Yext Hitchhikers Platform
When it comes to choosing a hosting strategy for your Yext Pages, we typically recommend hosting via subdomain, such as locations.brand.com. Hosting via subdomain is straightforward, as it only requires a single CNAME record.
Alternatively, you may choose to host your pages at a subdirectory of your apex domain, such as www.brand.com/locations. Opting for this hosting strategy requires more work, as you must configure some sort of reverse proxy service at your origin to forward requests to Yext. Refer to the image below:
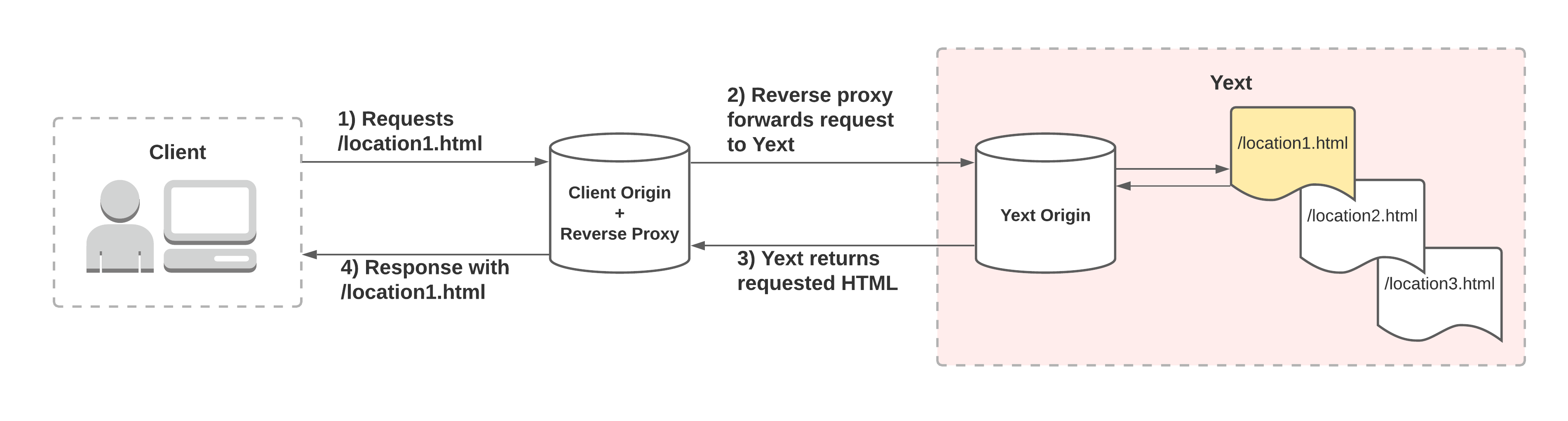
If you choose to use the subdirectory approach, below are the steps that we recommend when setting up the reverse proxy. For the sake of example, assume you would like to set up a reverse proxy for www.brand.com/locations.
1. Configure Yext Frontend Code
package.json
You must be using
@yext/pages
version 1.0.0-rc.9 or higher in order to reverse proxy. If you are on an older version, please refer to our
upgrade
guide to programmatically upgrade your repository.
vite.config.js
In your vite.config.js file, configure the
build.assetsDir
property as a combination of your desired subdirectory name and "assets". Refer to the example below:
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [react(), yextSSG()],
build: {
// prepend `assets` with your subdirectory name
assetsDir: "locations/assets"
}
});This configuration will instruct
Vite
to output all of your generated assets under locations/assets, as opposed to assets (the default).
config.yaml > reverseProxyPrefix
Next, you will provide a reverseProxyPrefix in your Pages configuration file, which stores the user-facing URL for your website. Pages uses this value to ensure that your site
redirects
,
sitemap
, and
OIDC
callback URL (if applicable) all work as intended.
In your config.yaml file, add two new blocks:
First, add a serving block, and set the reverseProxyPrefix property as the full URL of your subdirectory website. This step is necessary to ensure that your sitemap properly reflects the correct website URLs. Refer to the code snippet below:
serving:
reverseProxyPrefix: www.brand.com/locationsconfig.yaml > dynamicRoutes
Next, add a dynamicRoutes block with the following route below. This will ensure that requests for an asset from the client origin will resolve to the correct assets directory at the Yext origin.
dynamicRoutes:
- from: /assets/*
to: /locations/assets/:splat
status: 200 # 200 status indicates a URL RewriteAnalyticsProvider
Next, you need to ensure that the <AnalyticsProvider> component is configured to send requests when your pages load. To do so, configure the productionDomains prop to include your website domain.
Ensure that you are using
@yext/pages-components
version 1.0.0-rc.0 or higher.
Refer to the code snippet below:
const PageLayout = ({ children, _site, templateData }) => {
return (
<AnalyticsProvider
templateData={templateData}
productionDomains={["brand.com"]}
enableDebugging={true}
>
{children}
</AnalyticsProvider>
);
};
export default PageLayout;This will ensure that analytics events can only be triggered from brand.com/locations. You can confirm your analytics are working as expected by inspecting the Network tab in your browser. if you search for store_pagespixel, you will see analytics events firing with the isStaging property set to false.
![]()
2. Configure Root Domain
The reverse proxy should live on your domain, and forward traffic to the Yext-hosted domain, which which you just created in the previous step, and should look something like
[YEXT_HOSTED_DOMAIN].pgsdemo.comor[YEXT_HOSTED_DOMAIN].pagescdn.com.The subdirectory portion of the URL should be stripped out before forwarding the request to Yext Pages, e.g.:
- A request to
www.brand.com/locations/va/123-bob-ct.html - should forward to
[YEXT_HOSTED_DOMAIN]/va/123-bob-ct.html
- A request to
Set the proper redirect domain
- Ensure that the reverse proxy server sets a non-empty value (e.g.
true) for a custom header calledX-Yext-Reverse-Proxy, when forwarding requests to Yext. This allows Yext to detect that a request was sent from a reverse proxy, versus being sent from the domain itself. - When a non-null value for this header is set, Yext will compare the value set for
reverseProxyPrefixas defined in your config.yaml file against the reverse proxy origin URL. If they match, thereverseProxyPrefixvalue is used for the redirect post-OIDC authorization and for constructing absolute redirects returned to the reverse proxy. - (For OIDC implementations) The internal Pages backend system (which handles the OIDC) only receives traffic from the perspective of the Yext-hosted site (not the client-hosted reverse proxy site); as such, it is necessary to ensure that, when the OIDC authorization flow is initiated from the client-origin reverse proxy, the oath callback URL with the
reverseProxyPrefixis included in the list of redirect URLs in the IDP.
- Ensure that the reverse proxy server sets a non-empty value (e.g.
Set authorization session cookie
- Yext will always set the session cookie on the Yext origin domains. The reverse proxy will need to forward the cookie or set proper CORS headers to accept cookies from the origin domain.
- This means that all Yext domains will work by default, but that CORS headers/forwarding will need to be set up to set the cookie on the reverse proxy’s domain.
The reverse proxy should be configured to communicate with the hosting domain over HTTPS with SNI support. Without SNI support, your reverse proxy will not be able to communicate with Yext Pages hosting using HTTPS.
The Pages infrastructure requires that the HTTP “Host” header is set to the Yext Pages content host of
[YEXT_HOSTED_DOMAIN]. Any other Host header will prevent the Yext CDN from finding the proper content.The Yext bridge domain resolves to a dynamic set of IP addresses for our CDN. Please make sure that the DNS resolvers for your proxy respect DNS TTL values and that no IP pinning is being performed, as it is not supported.
- Your bridge domain can be found in the platform by navigating to Pages > Domains.
Client IP addresses should be forwarded using the standard HTTP
X-Forwarded-Forheader. Most web servers with reverse proxy functionality built in will handle this automatically. This is required for server-side geolocation to function properly.The reverse proxy should be configured to NOT cache any responses from Yext Pages, error or otherwise. That is, every request made for a Yext Pages content by a consumer should be forwarded to the Yext Pages content host. The Yext CDN has extensive caching logic in place; additional proxy-side caching could lead to stale consumer-facing content.
The reverse proxy should be configured to redirect any inbound URLs containing trailing slashes “/” to their equivalent URL without the trailing slash.
- The trailing slash is critical to ensure that relative URLs (assets and links) on the Yext Pages will resolve correctly.
- For example:
www.brand.com/locations/search/?query=new+yorkshould be redirected towww.brand.com/locations/search?query=new+york
- ⚠️ The one exception to this rule is the root domain, which should be configured to redirect to
www.brand.com/locations/. For example:www.brand.com/locationsshould be configured to redirect towww.brand.com/locations/
Yext Pages automatically maintains an up-to-date sitemap at
[YEXT_HOSTED_DOMAIN]/sitemap.xml. The public facing address of the sitemap will therefore bewww.brand.com/locations/sitemap.xml.- To expose the sitemap to search engines, the
robots.txtor existing sitemap ofwww.brand.comshould be updated to reference thewww.brand.com/locationssitemap. This ensures crawlers inspecting your root have a direct linkage to your Yext Pages sitemap. - If necessary, refer to our Sitemaps reference doc to customize your sitemap name.
- To expose the sitemap to search engines, the
If your reverse proxy requires the use of Content Security Policy (CSP) headers, ensure that the following Yext domains are whitelisted by your organization:
https://*.yext.comhttps://*.yextapis.comhttps://*.yextevents.comhttps://www.yext-pixel.comhttps://*.mktgcdn.com

