Maps | Yext Hitchhikers Platform
Maps are an important visual indicator to add useful context for location-type results. We can add a map to both the Universal and Vertical page for any entity that has an “Address” field stored. The address field in Content also stores the geocode, or the latitude and longitude, of the entity. These geocodes can be passed to different map providers to visualize the location on a map.
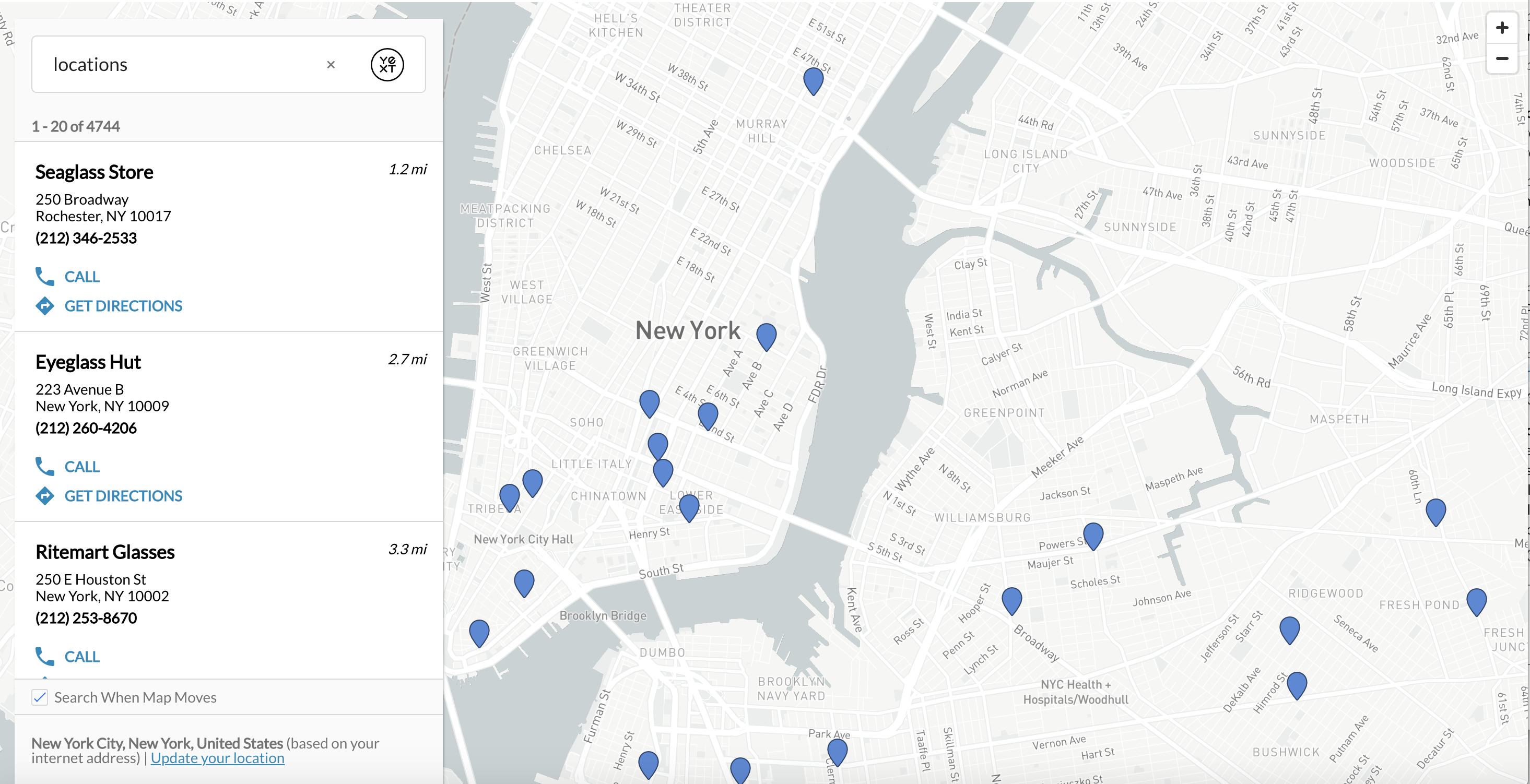
Whether it’s shops, healthcare professionals, restaurants, ATMs, or jobs, the map is often a crucial component of the page. Search supports a full-page maps experience on vertical search. Besides the fullscreen look, the layout (called vertical-full-page-map) includes interactivity between result cards and maps pins, as well as a maps display on mobile.
Note that the following information refers to the vetical-full-page-map. We’d recommend using this in favor of the deprecated vertical-map layout.
Universal Map Example
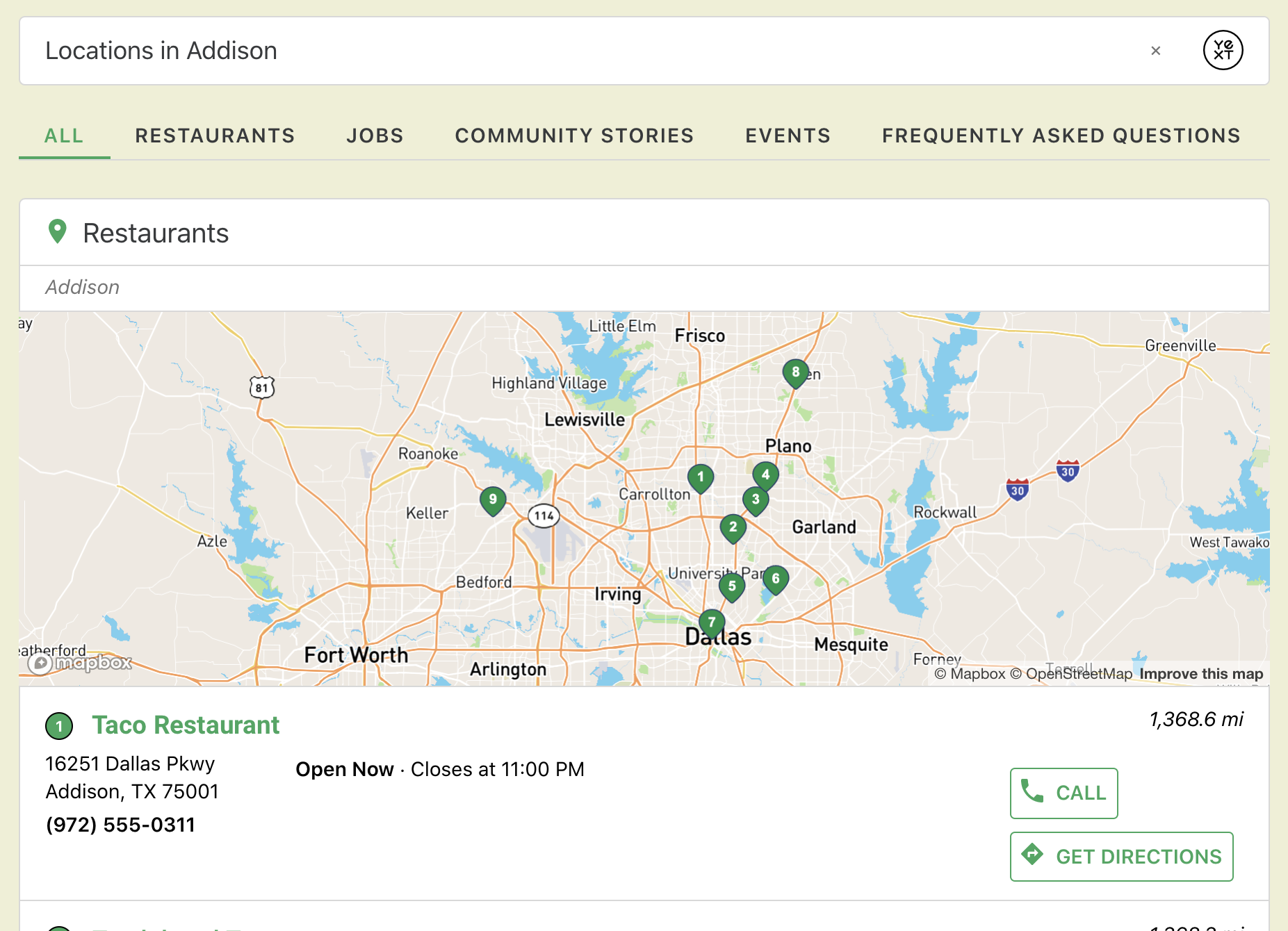
Vertical Full-Page Map Example
The Map Config
You’ll find the map config in the verticalsToConfig object. Set the behavior on the vertical here, and the universal page will inherit those same traits.
Alternatively, if you would like to change any map behavior on universal, you would need to define the attributes for your verticalKey in the Universal (typically index.json verticalsToConfig object.
"verticalsToConfig": {
"restaurants": { // The vertical key from your search configuration
// "label": "", // The name of the vertical in the section header and the navigation bar
"cardType": "location-standard", // The name of the card to use - e.g. accordion, location, customcard
"icon": "pin", // The icon to use on the card for this vertical
"mapConfig": {
"mapProvider": "MapBox" // The name of the provider (e.g. Mapbox, Google)
}
}
}Map Providers
We offer two different Maps providers that can accept those geocodes and render them on a map - Google Maps and Mapbox. Both accept these coordinates, as well as some other attributes, via an API.
Mapbox
Mapbox is a popular maps provider that abides by WCAG 2.0 AA best practices . For this reason, our sites default to MapBox. Behind the scenes, we use the Mapbox JavaScript API to surface results.
To use Mapbox, set your mapProvider to MapBox :
"mapConfig": {
"mapProvider": "MapBox", // The name of the provider (e.g. Mapbox, Google)
// "apiKey": "" // This is provided by the theme, unless you would like to use your own
},Google Maps
We use
Google’s Maps Javascript API
to surface results on a Google Map. To use Google Maps, set your mapProvider to Google :
"mapConfig": {
"mapProvider": "Google", // The name of the provider (e.g. Mapbox, Google)
// "apiKey": "" // This is provided by the theme, unless you would like to use your own
},Map and Card Size Configuration
When configuring your Maps, it’s important to consider the height and width of the map, results and cards. We’ve set these variables to reasonable defaults, but we’d recommend configuring them in certain scenarios.
Map Height
By default, Maps are meant to work well with the JS snippet integration option. Tweak the height in the following scenarios:
A. If you’re using the JS snippet integration option and the height of your header/footer is above or below average. We’d recommend viewing the map on the final page, and updating the --yxt-maps-desktop-height and --yxt-maps-mobile-height variables to make sure the map is fully visible in both scenarios.
--yxt-maps-desktop-height: 820px;
--yxt-maps-mobile-height: 620px;B. If you’re using the Yext-hosted integration option and the Map is not within an iframe. Update the height of the map to be the full view port (100vh) using the --yxt-maps-desktop-height and --yxt-maps-mobile-height variables in your answers-variables.scss.
--yxt-maps-desktop-height: 100vh; // default is 820px
--yxt-maps-mobile-height: 100vh; // default is 620pxCard Height
On the mobile map view, clicking a pin will display a card at the bottom of the screen. Depending on the amount of information in your card, you may want to update this height to insure the CTAs are displayed, or to remove excess space at the bottom. You can tweak this using the --yxt-maps-mobile-detail-card-height in your answers-variables.scss.
--yxt-maps-mobile-detail-card-height: 225px;Results Container Width
Based on the type of entity, adjust the width of your results container based on the importance of physical location to that entity’s profile.
For example, when users are searching for doctors, they likely care about the details of the doctor, while the doctor’s office location is secondary. In this case, the map can take up less of the screen real estate, to make room for wider, more in-depth results cards. Conversely, for gas stations with similar service, proximity to the user is the strongest factor in picking a location to visit, and the map should therefore take up the bulk of the screen.
The results container width is configurable via the --yxt-maps-desktop-results-container-width variable in the your answers-variables.scss.
--yxt-maps-desktop-results-container-width: 410px;Mobile Map Height
By default, the Navigation component is included in the Maps layout. However, if you would like to remove it (or if you have other components included in the header on mobile), update the map results header height to reach the top of the screen. The height is configurable via the --yxt-maps-mobile-results-header-height variable in your answers-variables.scss. Here’s how you’d update it if you are removing the Navigation component, for example:
--yxt-maps-mobile-results-header-height: 121px; //defaults to 185pxSimilarly, you may want to tweak the height of the footer if you remove or add different components. This can be updated with the --yxt-maps-mobile-results-footer-height variable in your answers-variables.scss.
--yxt-maps-mobile-results-footer-height: 97px;Recommended Default Configuration
Maps were built with the following recommended configurations:
Default Initial Search
When a user arrives on the Map vertical, they should see all locations displayed by default. This will help guide them to use the map, and help them understand the scope of the locations available.
In your config.json file, update the top level pageSettings to include the search property. You can learn more about this in the
Edit Page and Component Settings unit
.
"pageSettings": {
"search": {
"verticalKey": "locations", // The vertical key from your search configuration
"defaultInitialSearch": "" // Enter a default search term
}
},No Results
On most verticals, we recommend showing all results when there are no results returned. For the vertical-full-page-map layout, our user testing demonstrated this was not an intuitive experience; often, users wanted to use the map to exit the no results scenario (by moving the map and searching a different area), and showing all results in that context was confusing. We’d therefore recommend leaving your mapConfig to displayAllResults: false (as it is by default).
However, if you’d like to experiment with showing all results, set displayAllResults: true in your mapConfig. You’ll also want to set displayAllResults to true in your VerticalResults object, which you can learn more about in the
Display All Results on No results reference doc
.
"mapConfig": {
...
"noResults": {
"displayAllResults": true
}
...
},Overriding the no results template for the vertical-full-page-map layout is slightly different than other components, since the Map component lives entirely in the theme. To override, shadow theme-components/vertical-full-page-map-alternative-verticals/alternativeverticals.hbs and make any adjustments there.
Common Map Properties
There are several properties of the map you can set - if you’re using the vertical-full-page-map layout, we’ll walk through the most commonly used properties below.
enablePinClustering
Pin clustering is when two or more map pins that are close to each other are clustered together. When enabled, the pins will group together and indicate the number of pins in that area like so:
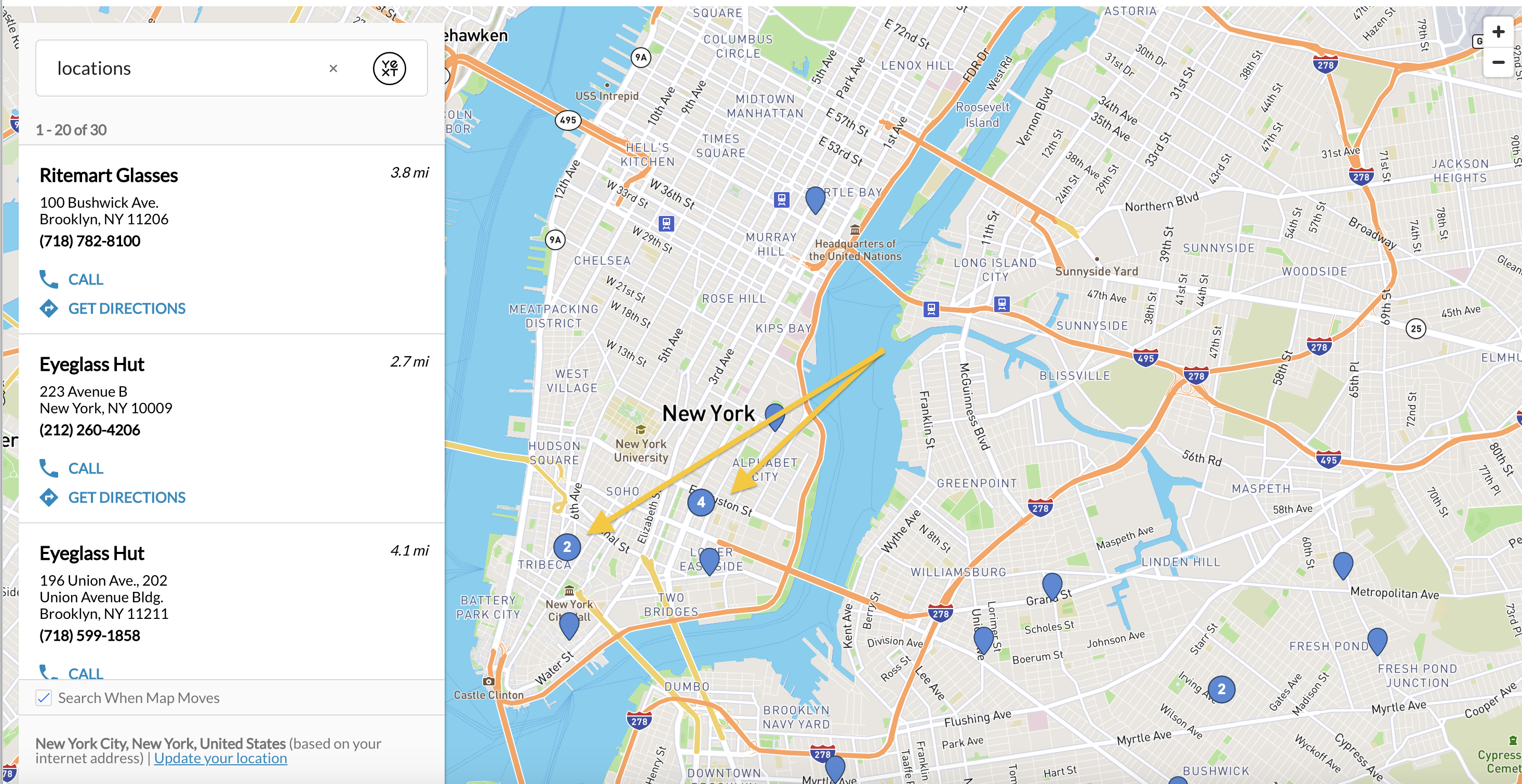
This attribute is false by default but if you would like to enable pin clustering, simply uncomment the field under verticalsToConfig and set it true.
"mapConfig": {
"enablePinClustering": true,
...
},disableSearchOnMapMove
By default, when you move the map, it will re-search the area. This attribute controls whether this will happen automatically. This field is set to false by default; however, a user can also uncheck this button themselves on the bottom left under “Search When Map Moves”.
By setting this to true, the “Search When Map Moves” box will be unchecked like so:
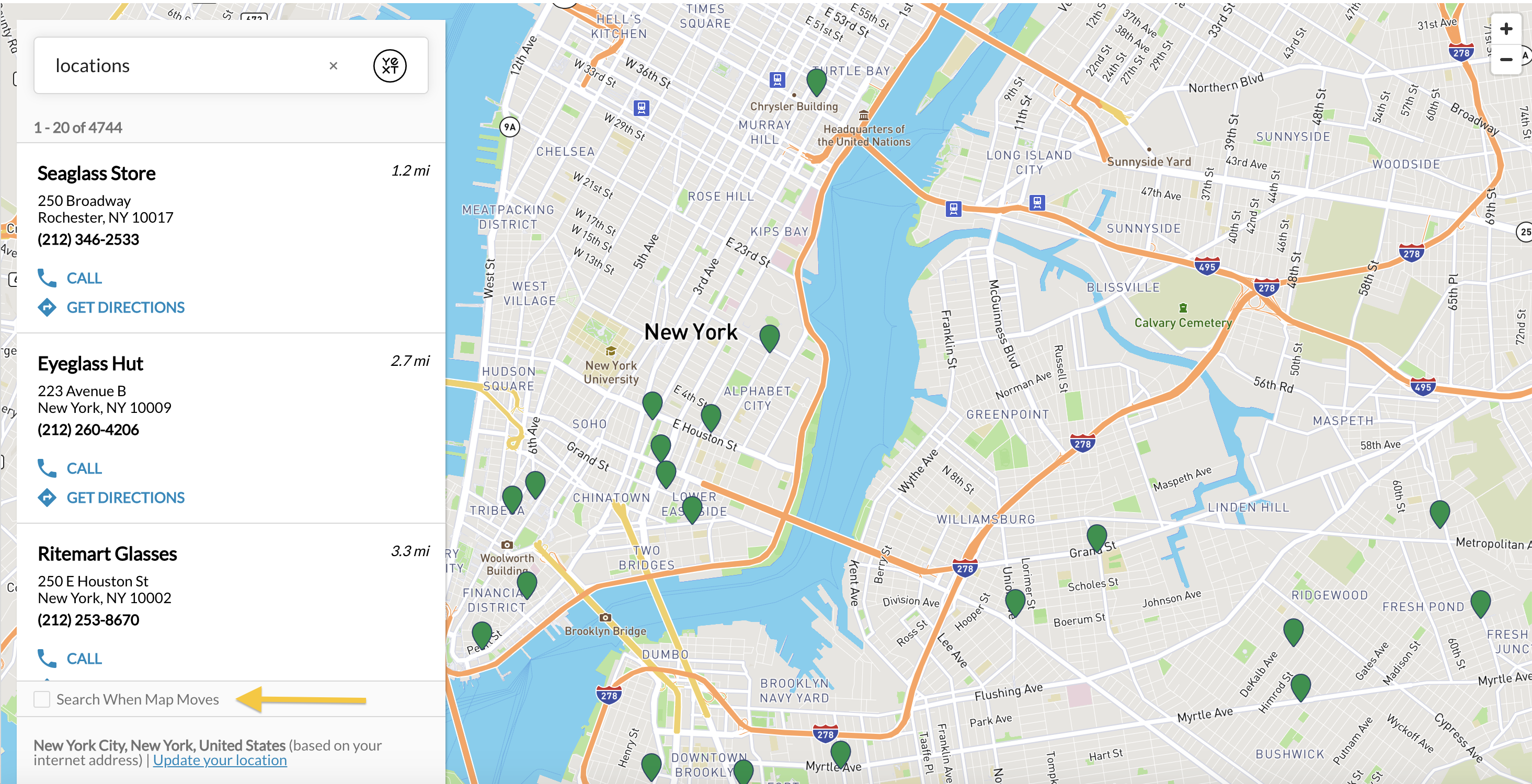
"mapConfig": {
"disableSearchOnMapMove": true,
...
},Provider Options
You can specify a JSON object to pass through to the map provider (Google or Mapbox) in your mapConfig. There are a number of options you can specify under providerOptions to pass through. See
Google Options
and
Mapbox Options
. If the options are not in JSON, they won’t be supported in this passthrough. We’ll cover a few useful options below.
Map Color and Style
You may want to customize the style or visual display for your map to match the aesthetic of your search configuration and website. To change this, pass the correct configuration in providerOptions for either Mapbox or Google. For example, Mapbox has several predefined styles. Here is one example “light” styling for Mapbox:
"mapConfig": {
"providerOptions": {
"style": "mapbox://styles/mapbox/light-v10"
}
...
},
zoom
The zoom level controls how zoomed in the map will be around a result. Our full page map will automatically zoom to a level appropriate for the number of pins returned so generally you won’t need to adjust this number.
Our maps have a default to a zoom level of 14, which surfaces a happy medium between a street and city level view. As you search or move the map to search, our maps will automatically adjust based on the number of pins.
However, you may want to adjust the default initial view without any search query. You will discover that smaller numbers are more zoomed out, while larger numbers are zoomed in. Set it in your Map config with the zoom parameter within providerOptions.
"mapConfig": {
"providerOptions": {
"zoom": 14
}
...
},You might think a smaller zoom may always be better, so you can be sure to see as much of the map as possible. However, that may not be super helpful to your users…see below for an example of a zoom level set to 1.
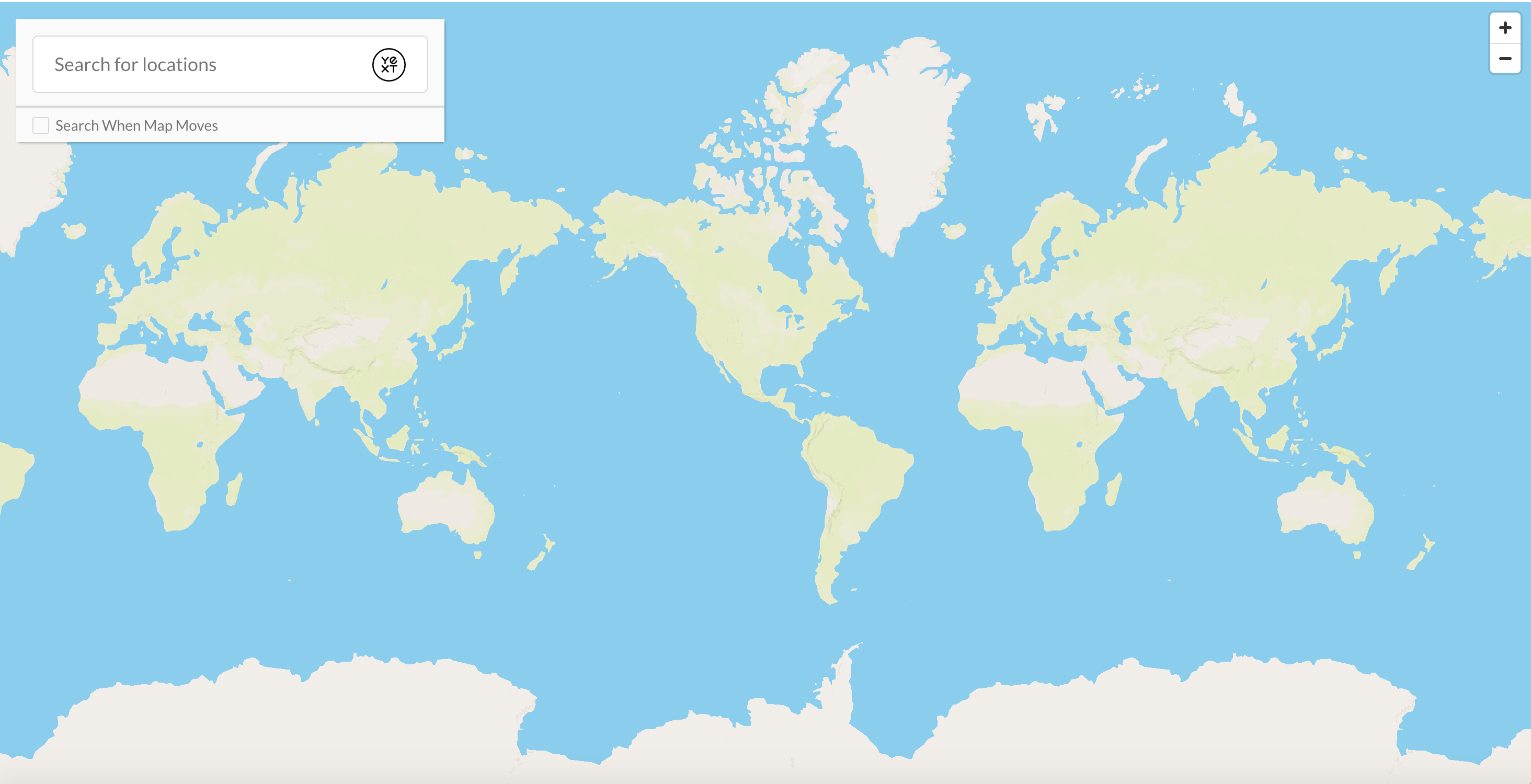
Alternatively, you might think zooming in as much as possible will give more details to a user, making it easier for them to find a location. You’ll find that this might make it harder for a user to understand the context of a location’s surroundings - see below for an example of a zoom level set to 15.
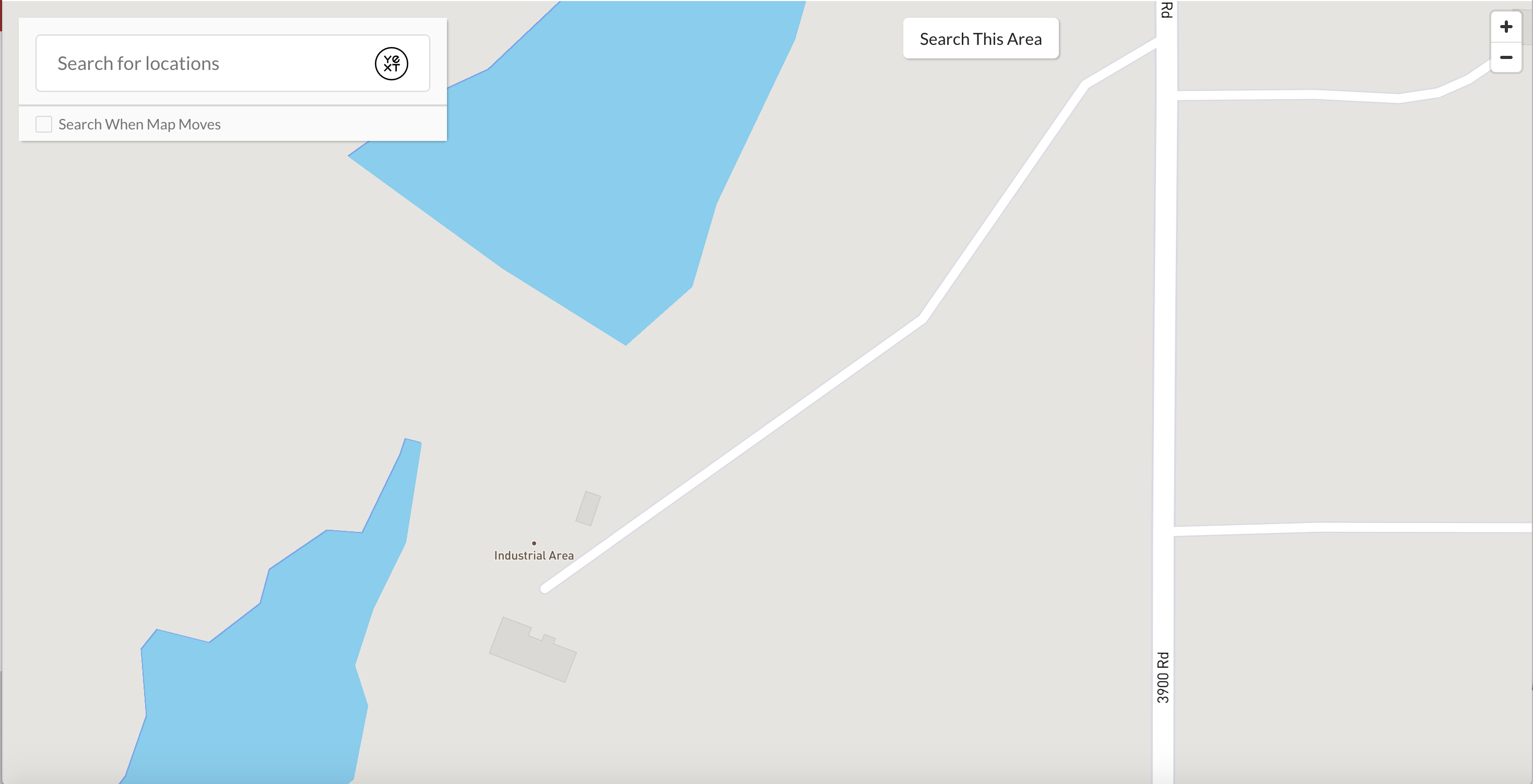
Feel free to play with the zoom levels. You can also see the general guidelines for each map provider below to understand what features would be visible at different zoom levels.
Google Zoom Level Descriptions
| Zoom Level | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | World |
| 5 | Landmass/Contintent |
| 10 | City |
| 15 | Streets |
| 20 | Buildings |
MapBox Zoom Level Descriptions
| Zoom Level | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | The Earth |
| 3 | A continent |
| 4 | Large islands |
| 6 | Large rivers |
| 10 | Large roads |
| 15 | Buildings |
scrollToZoom
When users interact with the map, scrolling over it will have different default behaviors depending on your map provider. For Mapbox, it will zoom in the map, and for Google Maps, it will display a message that describes how to zoom in. If you’d like to change that functionality for either provider, you can set it via the Mapbox and Google Maps options, for example:
"mapConfig": {
"providerOptions": {
"scrollwheel": true
}
...
},
